CLRI Scientists Develop Smart Nanozyme for Safe Energy Production
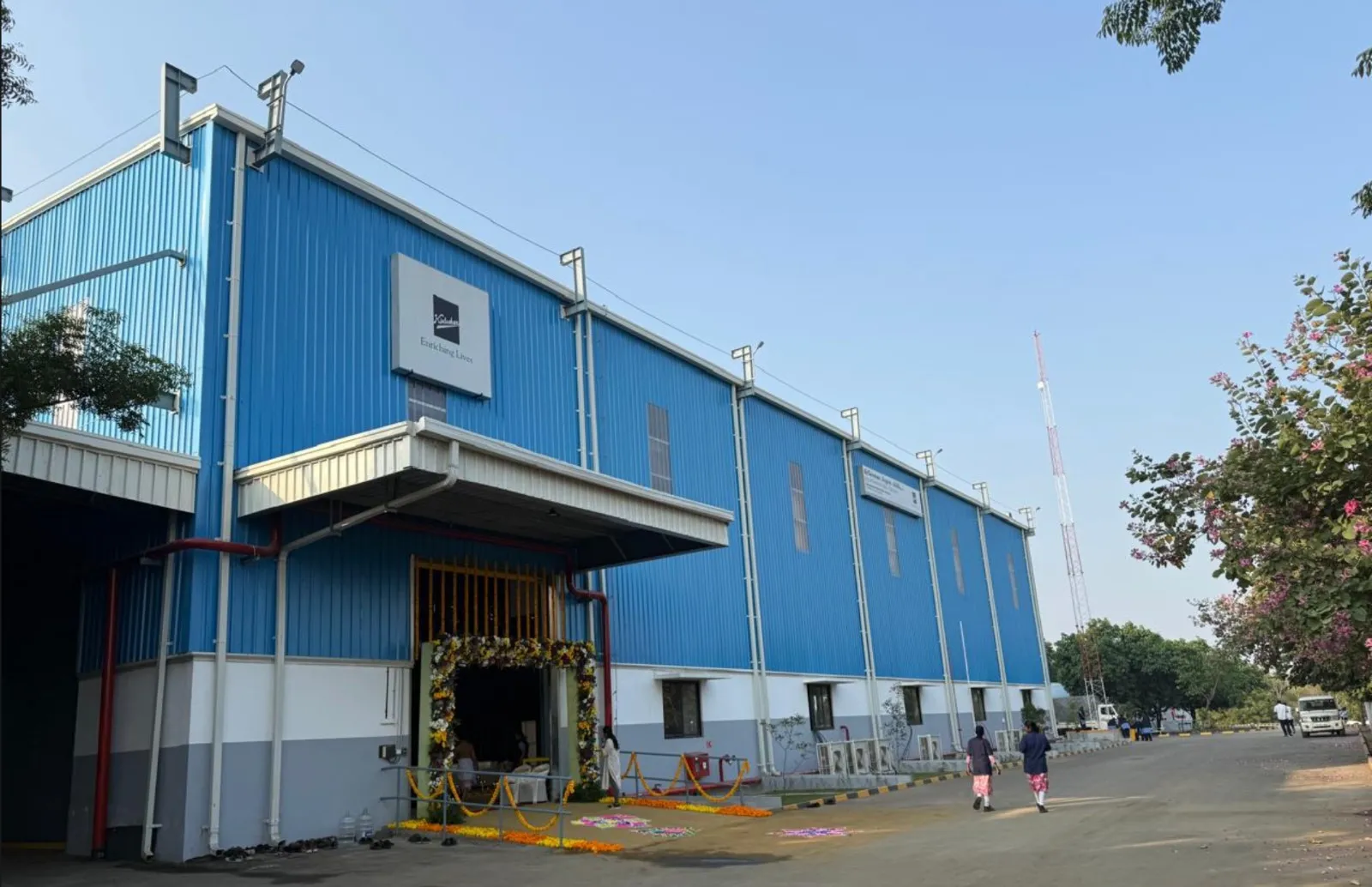

KBL Expands Kaniyur Facility in Centenary Year
Kirloskar Brothers (KBL), a leading player in fluid management solutions, has inaugurated a new factory building at its Kaniyur Manufacturing Facility in Tamil Nadu. The expansion coincides with a milestone year marking 100 years since the company manufactured and installed India’s first centrifugal pump in 1926. The newly commissioned facility is aimed at enhancing productivity and operational efficiency, enabling the company to address rising domestic as well as international demand while upholding stringent quality benchmarks. Sustainability remains a central focus of the expansion. Ar..
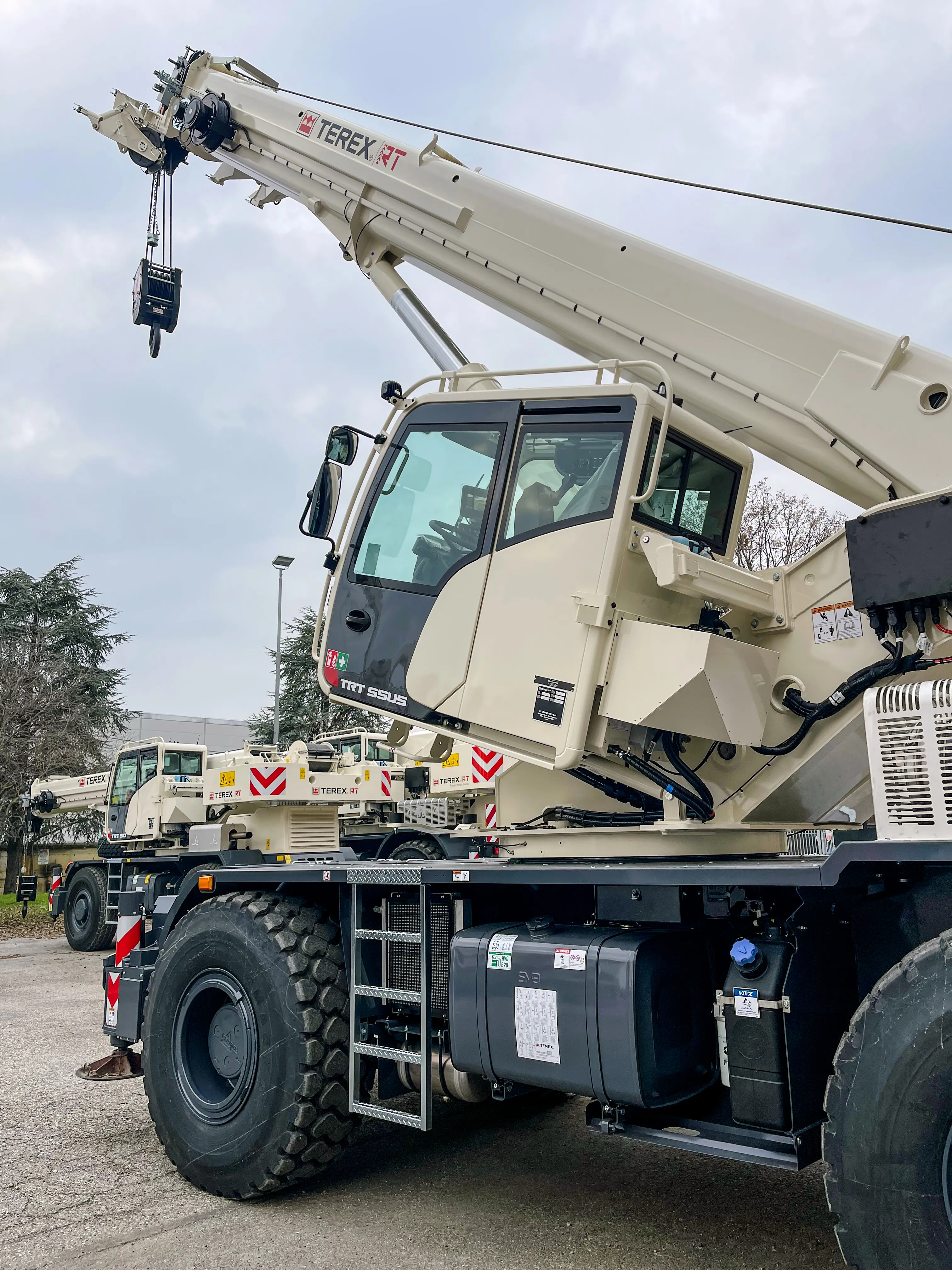

Raimondi to Debut TRT 55US at CONEXPO
"Raimondi Group will present the TRT 55US rough terrain crane at CONEXPO 2026, marking the first product debut under its newly established Raimondi North America operations hub.Developed by Terex Rough Terrain, now part of the Raimondi portfolio, the 55-tonne model has been engineered specifically to meet North American operational, regulatory and environmental requirements.Designed for North American ApplicationsThe TRT 55US features a compact transport-friendly design, an additional jib configuration and a redesigned operator environment aimed at improving efficiency and precision. It offers..

CPCL Ranks No.1 in NHAI DPR Ratings
"Chaitanya Projects Consultancy (CPCL) has secured the top position in National Highways Authority of India’s first-ever provisional DPR consultants rating, scoring 80.75 out of 100 and outperforming 55 peer firms.CPCL ranked ahead of Pentacle Consultants (78), L&T Infrastructure Engineering (76), MSV International Technology (74) and Transys Consulting (72). The ranking, released in the fourth week of January 2026, marks NHAI’s first transparent evaluation framework aimed at enhancing DPR quality under Bharatmala and other national highway programmes.The move aligns with the accountab..

















