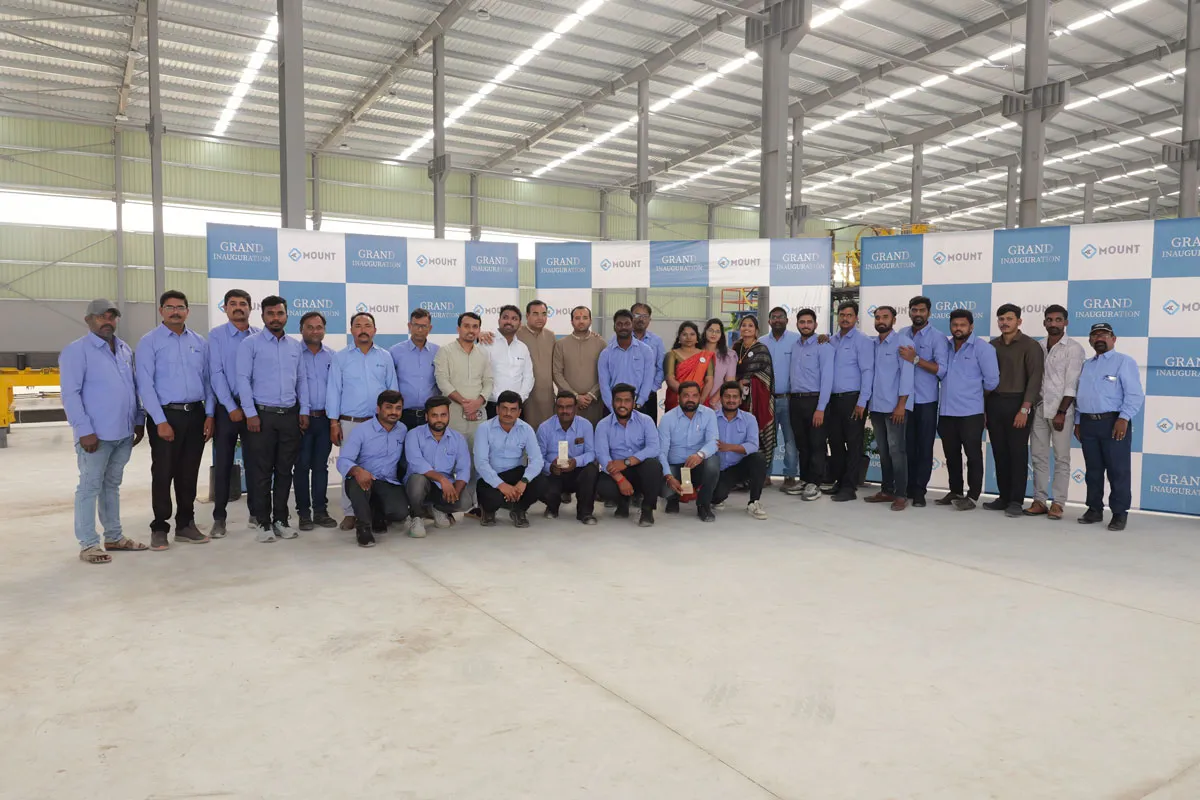

Mount Invests Rs 250 Cr, Adds PUF & PEB Plants, 400+ Jobs
TUMKUR, Karnataka, January 8, 2025 - Mount Roofing & Structures Private Limited, one of India's fastest-growing manufacturers in PUF and a leading solutions provider across Pre-Engineered Building (PEB) and Polycarbonate sheets, simultaneously inaugurated its second fully automated continuous Sandwich Panel manufacturing line and a new PEB manufacturing plant at its integrated campus in Tumkur." The milestone expansion, part of a total investment of INR 250 crores, marks a significant advancement in the company's commitment to engineered performance, manu..

Titan Intech Strengthens UltraLED Push With Global LED Veteran
Titan Intech has announced the induction of global LED industry veteran Su Piow Ko to its Board of Directors, marking a strategic step in strengthening its UltraLED Displays roadmap and building globally competitive LED display solutions from India.The appointment aligns with Titan Intech’s ambition to position India as a hub for advanced, high-quality LED display manufacturing. With an increased focus on UltraLED Displays, the company aims to enhance technical governance, raise manufacturing standards and expand its presence across global markets.Su Piow Ko brings over three decades of inte..

Dun & Bradstreet Flags New Growth Engines in India 2026 Outlook
Dun & Bradstreet has released its India 2026: D&B’s Perspective report, projecting a stable macroeconomic environment underpinned by fresh opportunities for productivity-led and inclusive growth. The report outlines how India’s next growth phase will be driven by digitised logistics, trusted data ecosystems, clean energy and rising city vitality.According to the outlook, India’s GDP growth is expected to reach around 6.6 per cent by FY2027, supported by resilient consumer demand and sustained public investment. Manufacturing is seen entering a new phase, moving beyond scale towar..
















