
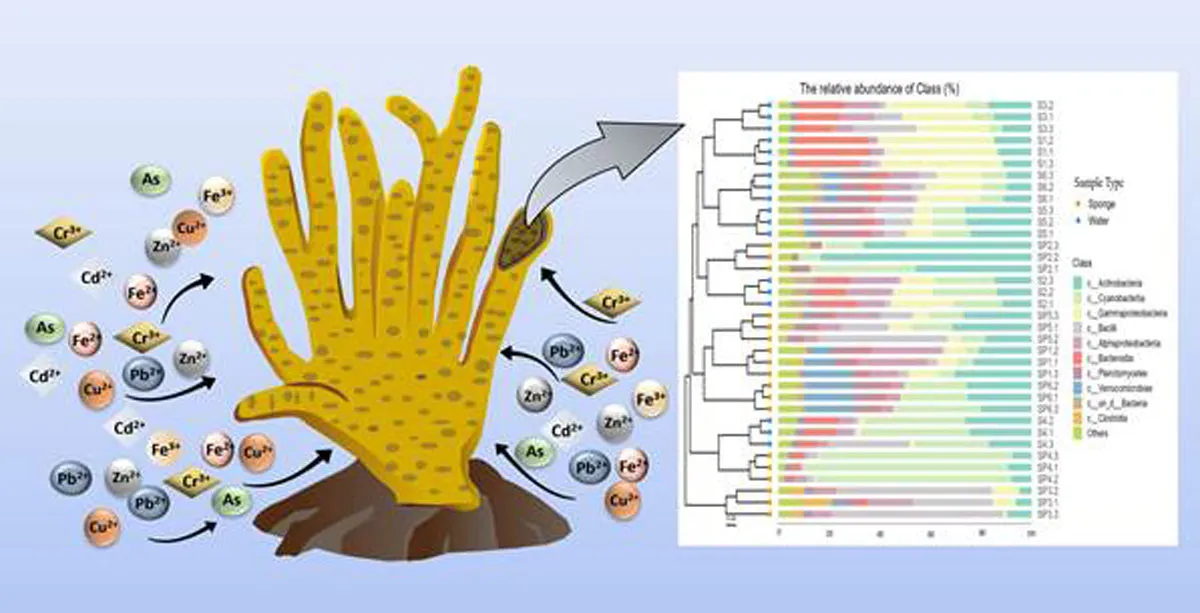
Study Highlights Freshwater Sponges’ Role in Fighting Metal Pollution
Scientists have identified freshwater sponges and their associated microbial communities as powerful natural allies in tackling toxic metal pollution, offering new hope for sustainable water quality management. A recent study has revealed that these sponges can act both as bioindicators and effective absorbents of harmful metals such as arsenic, lead and cadmium.The findings come from a study published in Microbiology Spectrum by researchers from Bose Institute, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India. The research focused on freshwater spong..

79% of Indian Railways Track now Supports Speeds of 110 Kmph+
Indian Railways has significantly enhanced the speed potential of its track network over the past decade, with 79 per cent of tracks now capable of supporting speeds of 110 kmph and above, compared with just 40 per cent in 2014. The improvement reflects sustained investment in track modernisation and maintenance aimed at faster and safer train operations.According to official data, large-scale upgradation works have been undertaken over the last 11 years to improve track quality and performance. Key measures include the use of heavier 60 kg rails, wider-base concrete sleepers, thick web switch..

Indian Railways Clocks 80% Punctuality Nationwide from Dec 8–14
Indian Railways has reported strong operational performance, achieving an overall punctuality of 80 per cent across the network during the period from December 8 to December 14. The achievement reflects sustained efforts by railway divisions to enhance efficiency and ensure reliable and timely services for passengers and freight users.According to official data, 37 railway divisions recorded punctuality levels exceeding 80 per cent during the review period. Notably, 22 divisions achieved punctuality above 90 per cent, while 10 divisions went a step further by crossing the 95 per cent mark, hig..
















