Buildings to store energy using innovative concrete-based battery

ABB to Invest Rs 6.25 Billion to Expand India Manufacturing
ABB recently announced plans to invest approximately Rs 6.25 billion ($75 million) in India during 2026 to expand its manufacturing footprint and research and development capabilities. The investment follows more than $35 million spent in 2025 and reflects the company’s continued focus on strengthening its ‘local-for-local’ strategy in the country.The investment will support ABB’s Electrification, Motion and Automation businesses and expand manufacturing capacity for infrastructure sectors such as renewable energy, metro rail, data centres and industrial applications. Approximately 300..
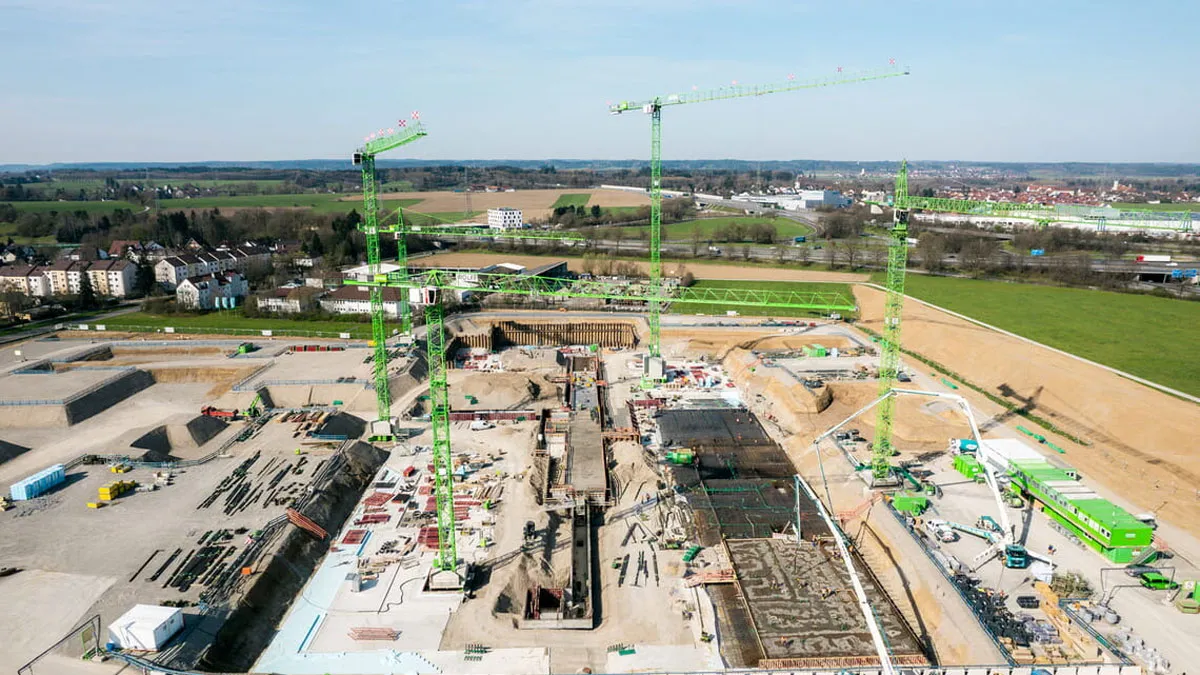

Six WOLFF Cranes Handle 60,000 m³ Concrete for German Hospital
Six WOLFF tower cranes are playing a key role in constructing a new hospital complex in Memmingen, Germany, supporting large-scale material handling for the project. The facility is being built on a 7.7-hectare site and will feature six floors, around 480 beds and a gross floor area exceeding 75,000 sq m.Building shell works began recently in February 2025. One WOLFF 6531.12 Cross crane supported early site preparation before being dismantled in autumn 2025, while five remaining cranes continue operations. Over an average deployment period of 16 months, the cranes are expected to move approxim..

REC Funds Rs 115.6 Million CSR Support for Bihar Eye Hospital
REC recently committed Rs 115.6 million under its Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) programme for the procurement of clinical and non-clinical equipment at Sankara Eye Hospital in Saharsa, Bihar. The initiative aims to strengthen healthcare infrastructure and improve access to specialised eye care services in the region.A Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) was recently signed between Pradeep Fellows, Executive Director (CSR), REC Limited, and Wg Cdr V. Shankar (Retd), Trustee and Executive Director of Sankara Eye Hospital, at the REC office in the SCOPE Complex, New Delhi.The support is expecte..

















