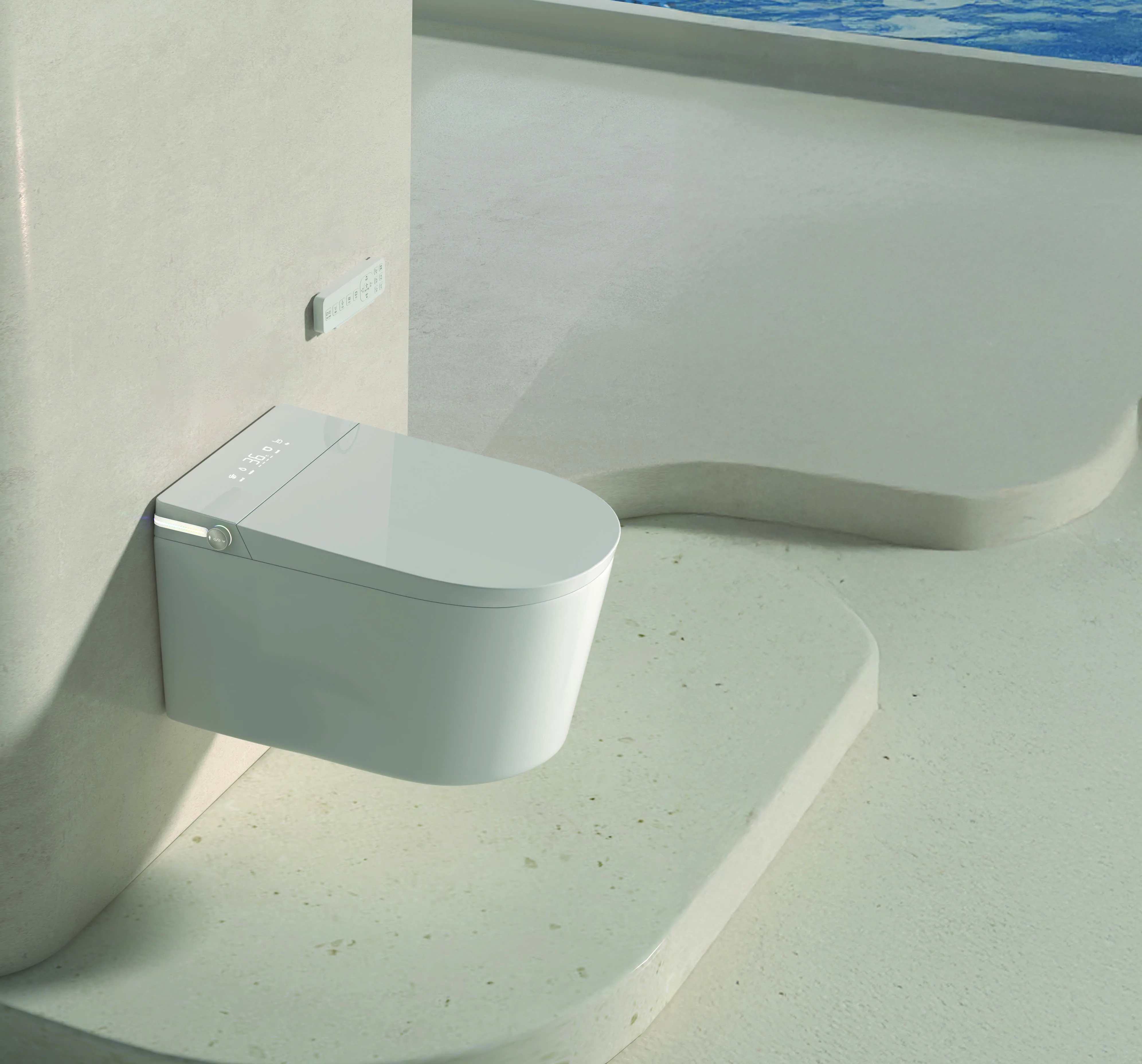


Hindware Introduces Starc Smart Wall Mount Toilet
Hindware has introduced the Starc Smart Wall-Mount Toilet under its Hindware Italian Collection, designed to combine automation, hygiene and contemporary bathroom aesthetics. The model features automatic flushing, sensor-based seat opening and closing, and remote-controlled functions. It also includes an oscillating water spray and warm air dryer for cleaning, along with a self-cleaning nozzle designed to maintain hygiene. Additional features include adjustable heated seating, customisable water temperature and pressure settings, a foot-touch flush system and an LCD control interface. The wa..
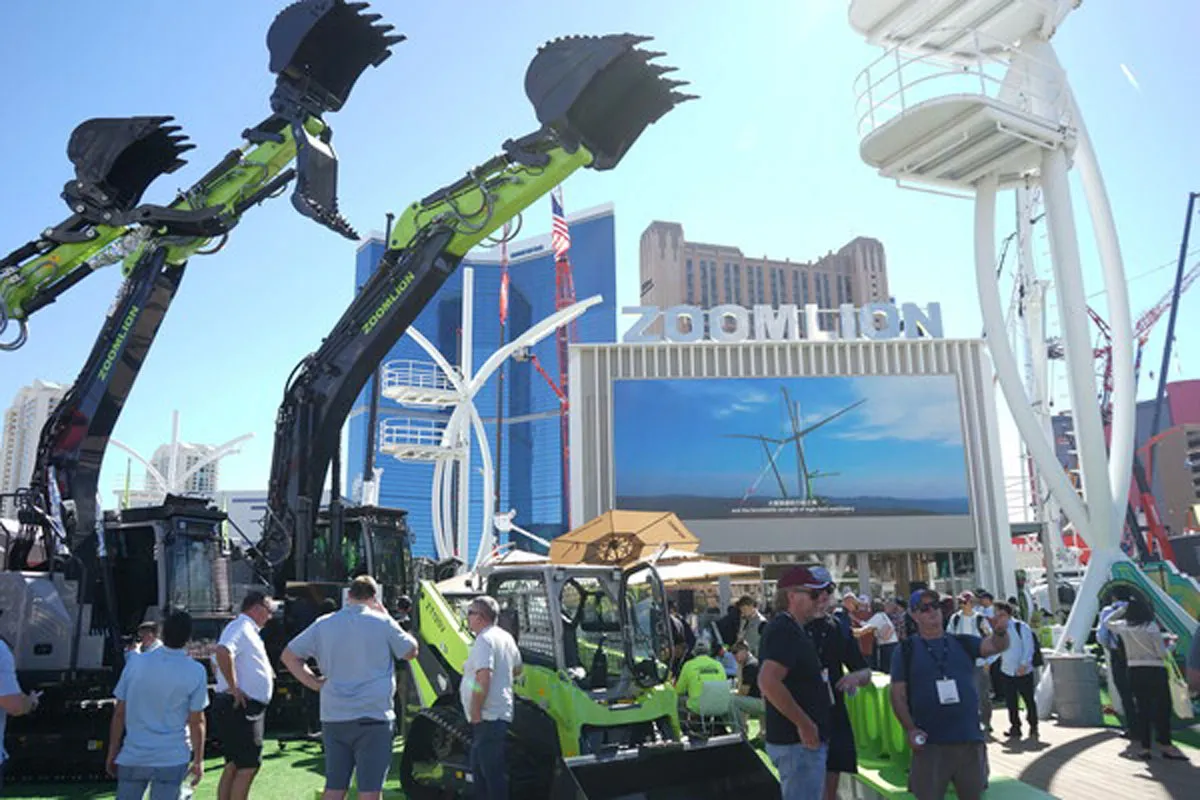

Company showcases North America-certified machinery and secures new deals
Zoomlion Heavy Industry Science & Technology Co., recently showcased a wide portfolio of North America-certified and customised construction equipment at CONEXPO-CON/AGG 2026 in Las Vegas. The display included engineering hoisting machinery, concrete equipment, earthmoving machinery, mining equipment and construction hoisting solutions tailored to regional operational requirements.All equipment presented at the exhibition complies with North American certification standards, with several models specifically developed to meet local regulatory requirements and site conditions. One of the hig..
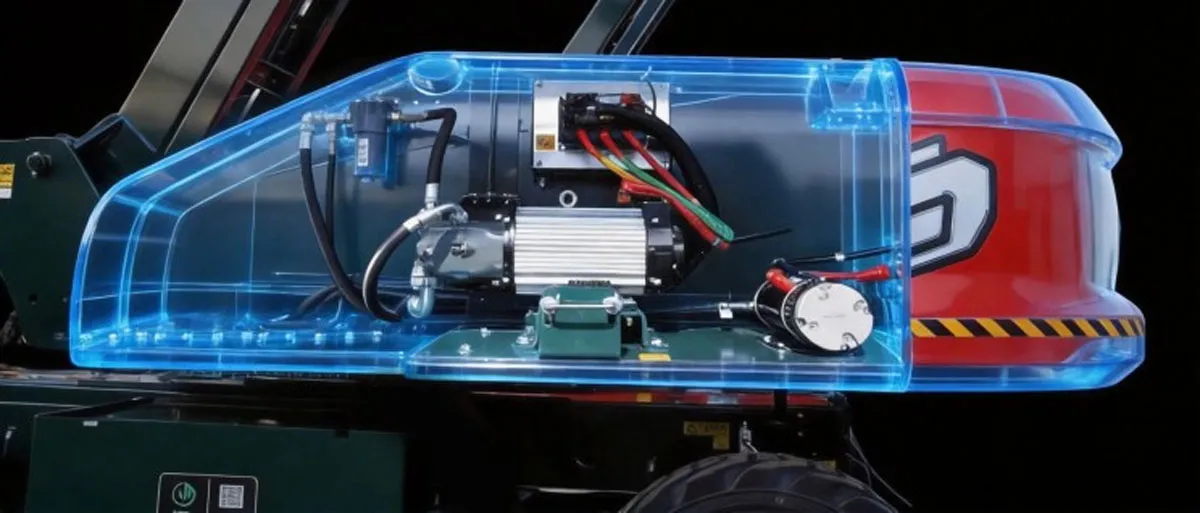
Sinoboom Launches Dual-ETM Smart Technology
Sinoboom recently introduced its Dual-ETM Smart Technology at CONEXPO-CON/AGG 2026, designed to enhance battery endurance and operational efficiency in electric boom lifts.The new technology integrates advanced components that enable real-time optimisation of power usage during equipment operation. By calculating the precise power requirement instantly, the system delivers only the energy needed for each movement, reducing the inefficiencies associated with conventional maximum-demand power systems.The solution incorporates multiple sensors—including pressure, weight, length and level sensor..

















