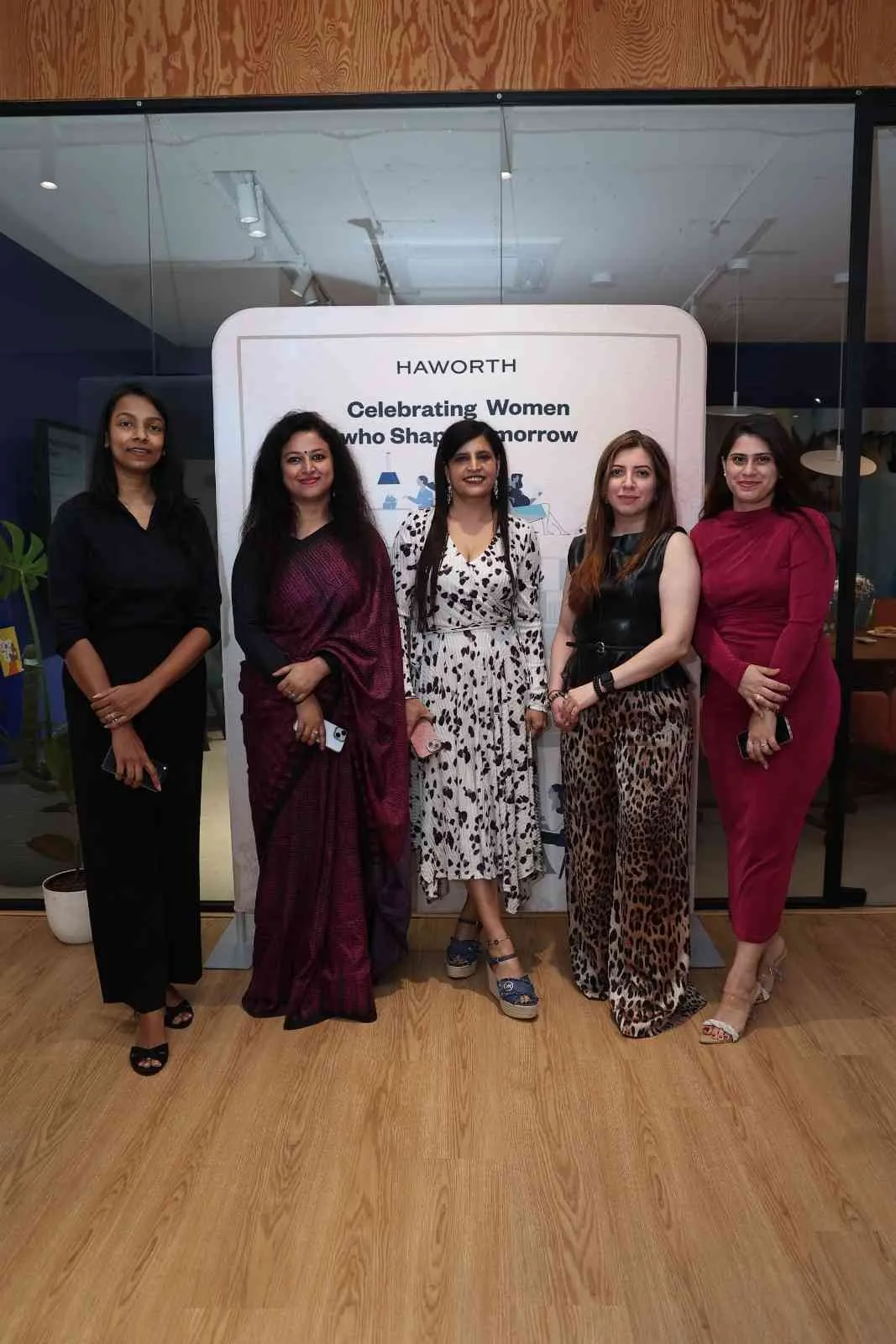

Haworth India Hosts Women’s Leadership Panel Series
Haworth India marked International Women’s Day by hosting a leadership roundtable series titled ‘Give to Gain’, bringing together senior women leaders from architecture and design firms, corporates and project management consultancies. The series has been conducted in Delhi and Mumbai, with upcoming sessions scheduled in Bengaluru and Hyderabad on 27 March 2026. Structured as moderated panel discussions followed by audience interaction, the initiative examined the business impact of women’s leadership and the role of inclusive workplaces in supporting professional growth. Manish Khan..

Max Estates Secures RERA For Max One Project
Max Estates has secured RERA approval (UPRERA No.: UPRERAPRJ9759) for its Max One development around Max Towers in Sector 16B, Noida, bringing renewed progress to a project previously stalled following the insolvency of its earlier developer. Spread across around 10 acres with an estimated development potential of about 2.5 million sq ft, Max One is planned as an integrated mixed-use campus combining serviced residences, premium offices, retail spaces and a private club. The project is expected to generate total sales potential of about Rs 20 billion along with an estimated annuity rental inc..
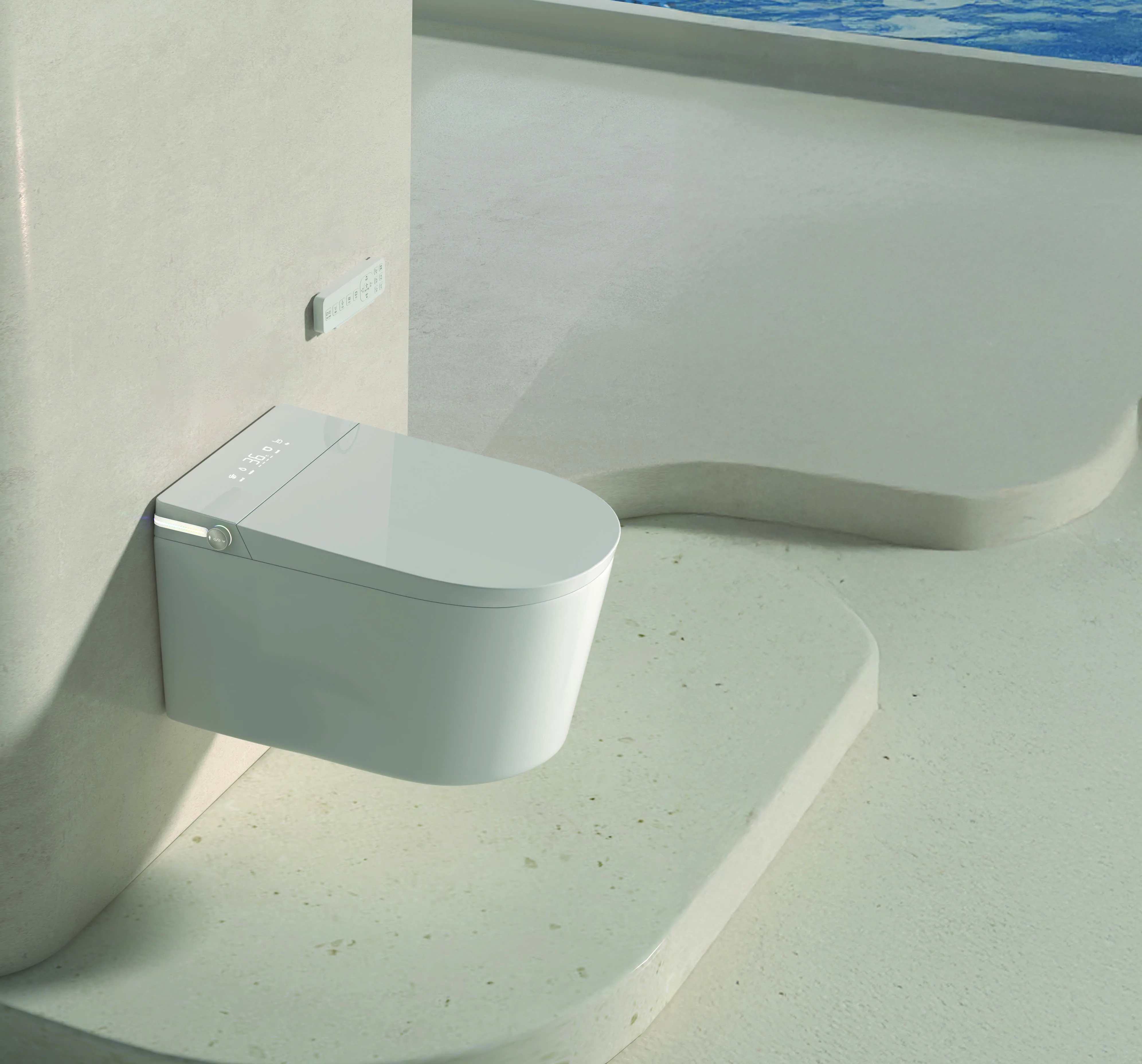

Hindware Introduces Starc Smart Wall Mount Toilet
Hindware has introduced the Starc Smart Wall-Mount Toilet under its Hindware Italian Collection, designed to combine automation, hygiene and contemporary bathroom aesthetics. The model features automatic flushing, sensor-based seat opening and closing, and remote-controlled functions. It also includes an oscillating water spray and warm air dryer for cleaning, along with a self-cleaning nozzle designed to maintain hygiene. Additional features include adjustable heated seating, customisable water temperature and pressure settings, a foot-touch flush system and an LCD control interface. The wa..

















