Metal-free Organic Catalyst Makes Hydrogen Fuel from Mechanical Energy
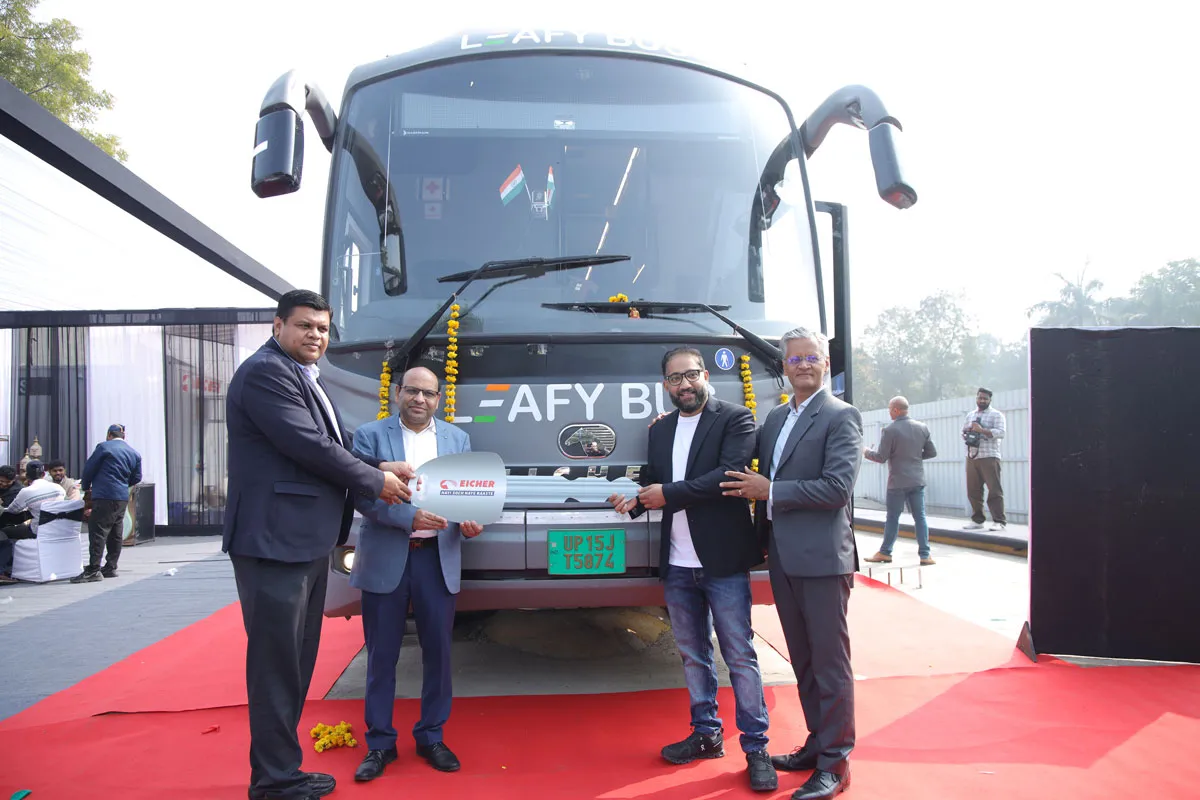

Eicher Delivers First 13.5 m Electric Intercity Sleeper Bus
Eicher Trucks & Buses, a business unit of VE Commercial Vehicles Ltd., has recently delivered its first 13.5 m electric intercity sleeper bus, marking a key milestone in India’s long-distance electric mobility segment. The first bus is being operated by LeafyBus, with plans to deploy 35 buses by March 2026 across high-demand intercity corridors in North India.The initial deployment will cover routes such as Delhi–Dehradun and Delhi–Lucknow, supporting LeafyBus’ expansion across environmentally sensitive and high-density travel corridors.Commenting on the partnership, Suresh Chettia..

HCSS Showcases Unified Construction Platform at CONEXPO 2026
HCSS will recently present the next evolution of its connected construction management platform at CONEXPO-CON/AGG 2026, bringing together construction workflows, data and teams on a single platform across the entire project lifecycle. The event will be held from 3–7 March 2026 in Las Vegas, Nevada. HCSS will host two booths at the show, demonstrating how its integrated software ecosystem enables seamless collaboration between the office, field and shop, from bid stage through to project closeout. Steve McGough, President and CEO, HCSS, said, “For 40 years, we’ve done everything within..

Berger Paints Q3 Profit Declines Despite Volume Growth
Berger Paints India has reported a mixed performance for the quarter ended 31 December 2025, with healthy volume growth and margin improvement offset by softer demand conditions and cost pressures. On a consolidated basis, revenue from operations for the quarter stood at Rs 29,840 million, compared to Rs 29,751 million in the corresponding quarter last year, reflecting a marginal increase of 0.3 per cent. EBITDA (excluding other income) was Rs 4,710 million, slightly lower than Rs 4,717 million a year earlier. Net profit declined by 8.3 per cent to Rs 2,713 million from Rs 2,960 million. Sta..

















