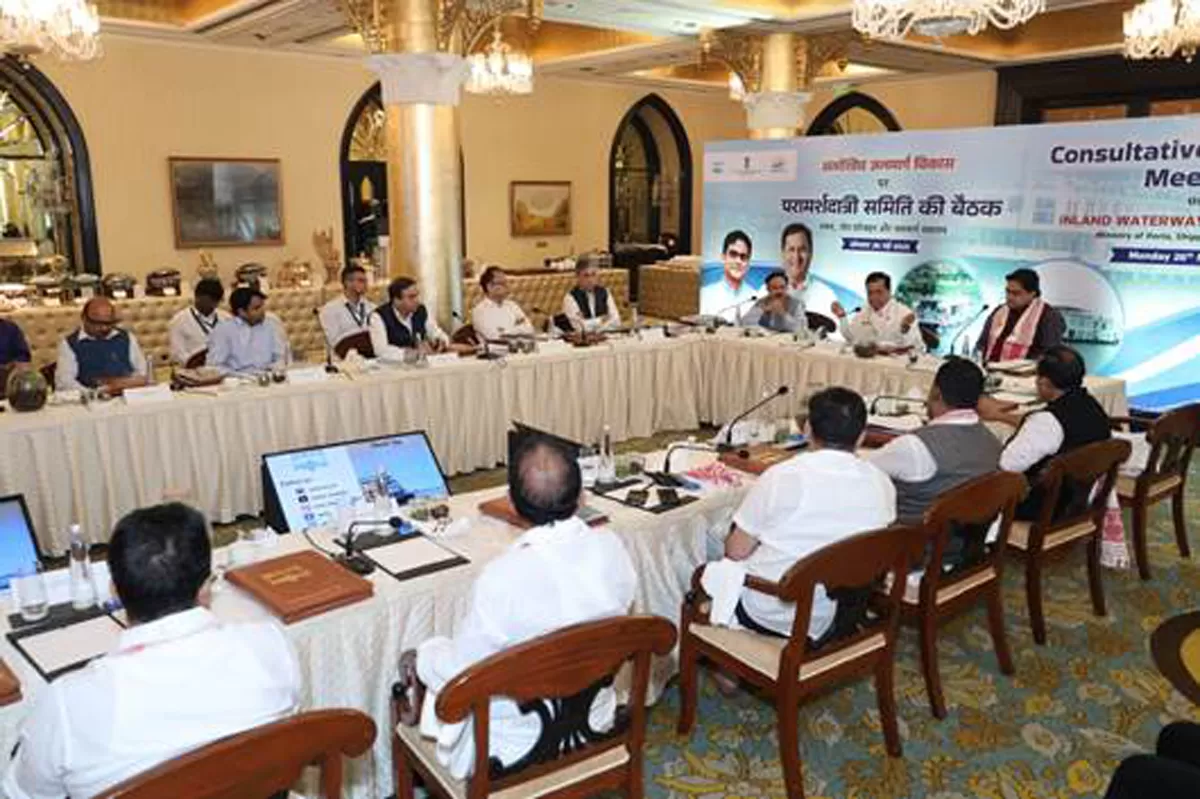
Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Sarbananda Sonowal, today chaired a meeting of the Consultative Committee on Inland Waterways Transport in Mumbai, where it was revealed that 76 waterways are targeted to be made operational by 2027, with cargo volume expected to surge by 156 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) by end of FY 2026. The Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), the nodal agency under the Ministry, presented a comprehensive review of major projects, future projections, and the roadmap ahead. Members of Parliament attending the meeting acknowledged and appreciated the progress made and supported increased budgetary allocations to boost the sector's growth.
The footprint of inland water transport is expected to expand significantly—from 11 states in FY 2024 to 23 states and 4 Union Territories by FY 2027. To support this growth, projects worth ₹1,400 crore were launched or announced during the Inland Waterways Development Council (IWDC) meeting held on January 10, 2025. Additionally, the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) is conducting 10,000 km of longitudinal survey each month to assess Least Available Depth (LAD) for improved navigability. Cargo Volume is likely to make an incremental growth up to 156 MTPA by March, 2026 inching closer towards the Maritime India Vision 2030 target of 200 MTPA.
Speaking on the occasion, the Union Minister Sarbananda Sonowal said, “Inland waterways are emerging as the watershed moment in India’s logistics and transport ecosystem. Under the visionary leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi we are witnessing a transformational shift with policy interventions like the National Waterways Act, 2016, the Inland Vessels Act, 2021 and supplemented by multiple programmes like Jal Marg Vikas Project, Arth Ganga, Jalvahak scheme, Jal Samriddhi scheme, Jalyan & Navic among others. Through Maritime India Vision 2030 and the Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047. These roadmaps are not just policy documents—they are catalysts driving India toward becoming a global maritime powerhouse. Today’s meeting with esteemed Members of Parliament reflects a unified commitment to boost infrastructure and unlock the immense economic potential of our rivers and coasts. With enhanced budgetary support and cooperative federalism, we are building a greener, more efficient, and future-ready waterway network across the country.”
The Regional Waterways Grid aims to boost economic activity by ensuring seamless vessel movement from Varanasi to Dibrugarh, Karimganj, and Badarpur via the IBP route, creating a 4,067 km economic corridor. A traffic study and DPR for renovating the Jangipur navigation lock are underway. The project’s cargo potential is estimated at 32.2 MMTPA by 2033.
On NW 1 (Ganga), a dedicated waterway corridor spanning 1,390 km is being developed to enable seamless movement of vessels, enhancing the efficiency of inland transport. As part of this initiative, capacity augmentation of NW-1 is underway to support the navigation of 1,500–2,000 DWT vessels, alongside the creation of key cargo handling facilities at Varanasi (MMT), Kalughat (IMT), Sahibganj (MMT), and Haldia (MMT).
Inland Waterways has major projects in the Northeast. A Rs 50 billion roadmap is planned over the next five years. On NW-2 (Brahmaputra), four permanent terminals—Dhubri, Jogighopa, Pandu, and Bogibeel—and 13 floating terminals are supported by fairway and navigation upgrades. A Rs 2.08 billion ship repair facility at Pandu and a Rs 1.80 billion alternative road are set for completion by 2026 and 2025, respectively. On NW-16 (Barak), terminals at Karimganj and Badarpur are active, while NW-31 (Dhansiri) is being developed to support NRL’s expansion.
Adding further, Sarbananda Sonowal said, “In line with the Harit Nauka Guidelines, the Inland Waterways Authority is committed to green and sustainable transport solutions, including the procurement of electric catamarans and hydrogen fuel cell-powered vessels. By strengthening urban water transport through water metro projects and promoting eco-friendly cruise tourism, we are paving the way for a cleaner, greener future in inland waterways transportation. The Regional Waterways Grid aims to seamlessly connect Assam and the Northeast with the rest of India through an integrated network of inland waterways. This will boost regional trade, tourism, and connectivity while unlocking economic potential across the Brahmaputra and Barak River systems. Government is also working on a ₹5,000 crore roadmap for Inland Waterways Development in Northeast Over Next 5 Years.”
The committee also reviewed the ongoing works on NW -1 (river Ganga), NW2 (Brahmaputra) among other states like Odisha, Jammu & Kashmir, Goa, Kerala, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.