Kumar Corp Launches Plumeria Project In Bengaluru
Kumar Corp has launched Kumar Plumeria, a premium residential development near KIADB Aerospace Park in Bengaluru. The project comprises six residential towers offering 3.5 BHK, 3.5 BHK with staff and 4.5 BHK with staff residences designed with expansive balconies, natural ventilation and landscaped surroundings. The development features saleable areas ranging from about 2,680 sq. ft. to 3,070 sq. ft. and is planned as a low-density community with around 100 residences. The project integrates a landscape master plan that includes open green spaces, community zones and recreational amenities. ..
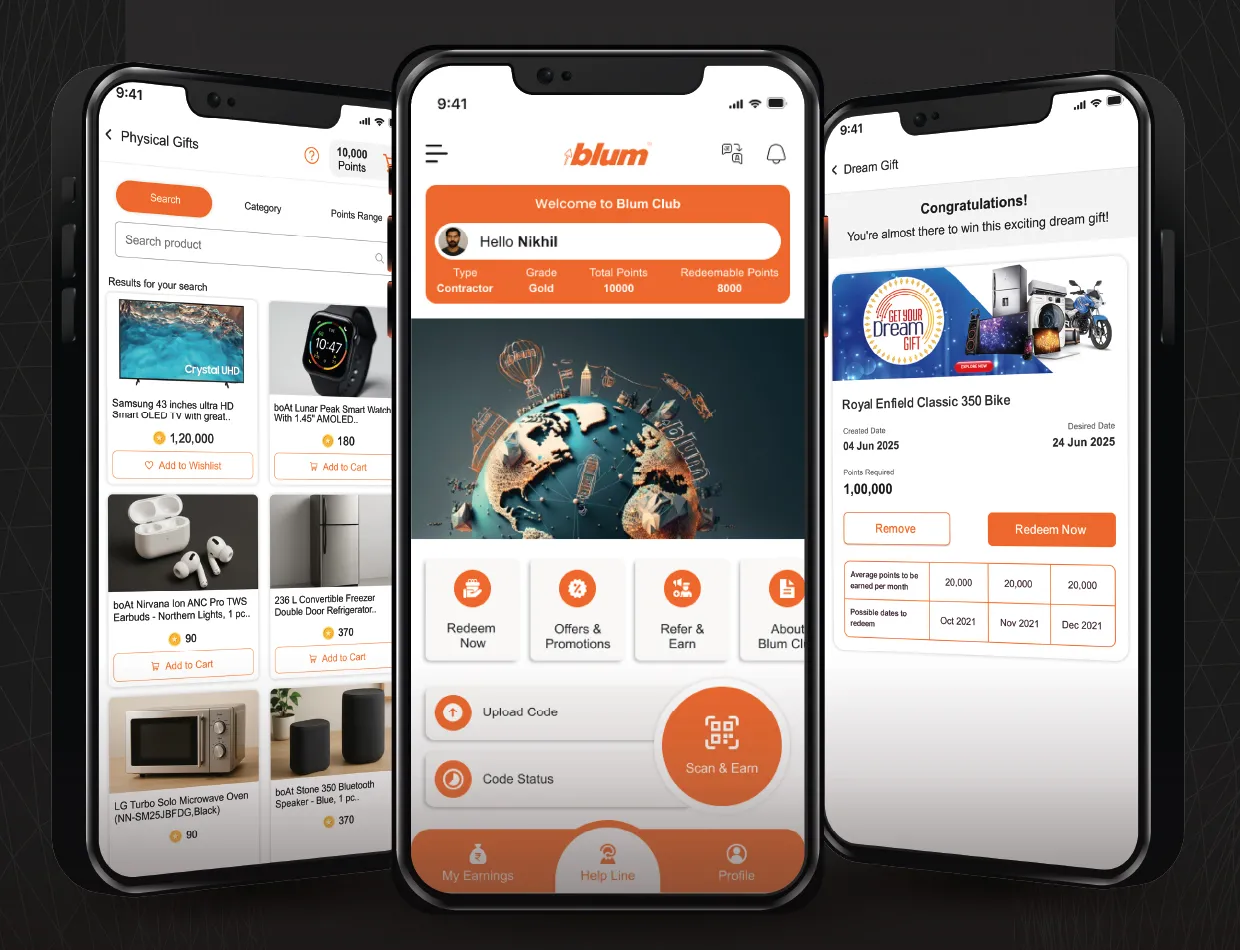
Blum India Launches Blum Club App
Blum India has introduced the Blum Club app, a loyalty platform designed for carpenters and contractors to recognise and reward their role in furniture installation and interior construction. The app allows users to scan QR codes on Blum product packaging to collect points linked to purchases. These points can be redeemed directly as monetary transfers to bank accounts through the platform’s redemption system. Neelam Shah, Head of Marketing and Communications at Blum India, said the initiative is aimed at recognising the contribution of craftsmen who install hardware products in residentia..

Enlight Metals Launches Waste Free Steel Procurement Model
Enlight Metals has introduced its Waste Free Steel (WFS) initiative, aimed at transforming steel procurement through precision-driven sourcing and advanced material planning. The programme seeks to reduce steel wastage by 8–10 per cent in infrastructure and EPC projects by shifting procurement practices from volume-based buying to drawing-based supply aligned with engineering requirements.The initiative is powered by Enlight Metals’ Agentic AI–enabled metal procurement platform, which enables project teams to submit technical drawings and material specifications for detailed analysis. Ba..