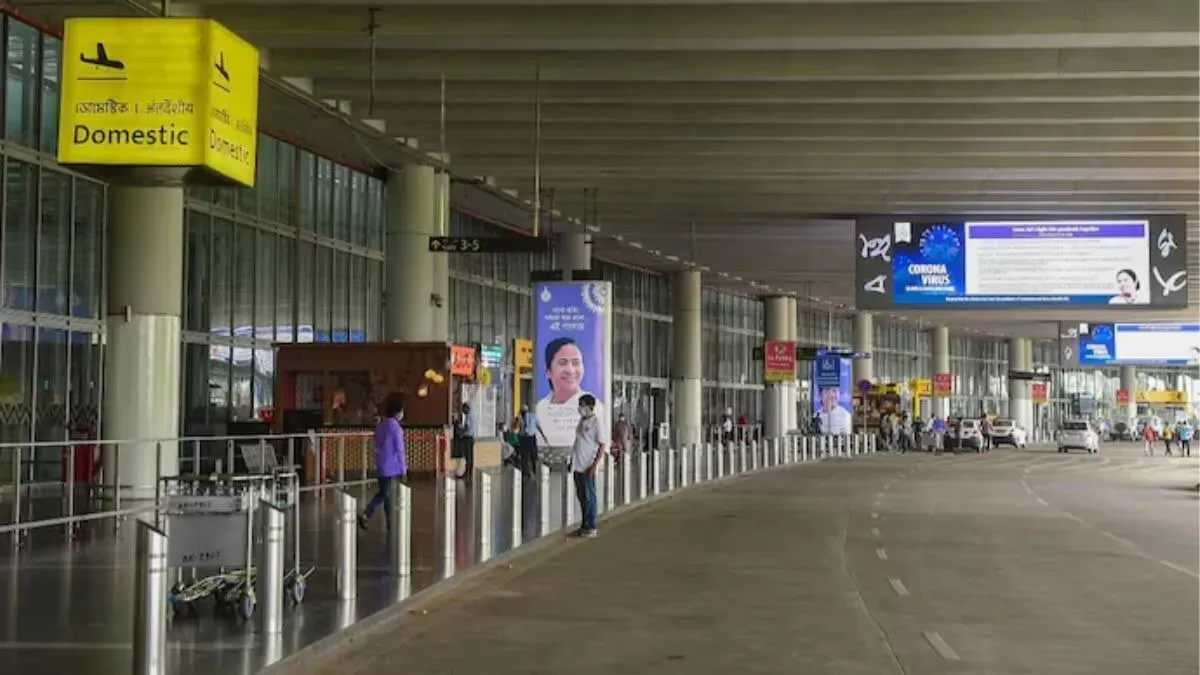
AAI Expands High-Rise Limits Near Kolkata Airport to 20 Km

BMW Industries partners with IOCL for PNG supply at Bokaro plant
BMW Industries has entered into a strategic partnership with Indian Oil Corporation (IOCL) for the supply of Piped Natural Gas (PNG), reinforcing its commitment to adopting cleaner and more efficient energy sources for its operations.The agreement was signed at the Eastern Region Pipelines (ERPL) headquarters in Kolkata. The partnership is expected to support the company’s upcoming manufacturing facility in Bokaro by facilitating the use of natural gas as a primary energy source.According to the company, the adoption of PNG will help enhance operational efficiency while also contributing to ..

Bombay Realty Secures RERA for Three ICC Tower in South Mumbai
Bombay Realty, the real estate arm of Bombay Dyeing and part of the Wadia Group, has received Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) certification for Three ICC – Wing A, the latest luxury residential tower at Island City Center in Mumbai’s Dadar.The RERA registration marks a key milestone in the development timeline and reinforces the company’s focus on regulatory transparency, timely project delivery, and high construction standards.Following the success of One ICC and Two ICC, the upcoming Three ICC tower represents the next phase of the Island City Center development. The project ai..
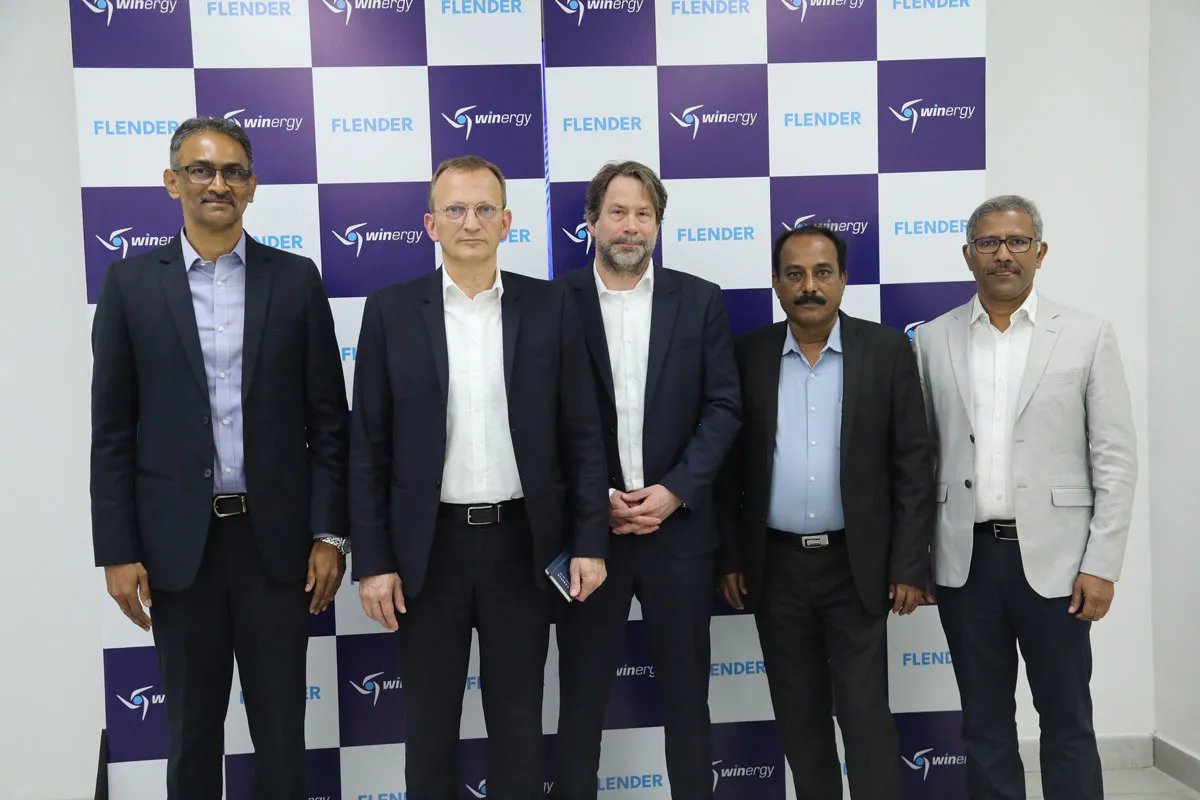

Flender launches India’s largest wind gearbox test rig in Walajabad
Flender has inaugurated a 13.5 MW wind turbine gearbox test rig at its Walajabad facility near Chennai, marking the largest installation of its kind in India. The new facility is expected to strengthen the company’s manufacturing and testing capabilities while supporting the growing demands of the wind power sector in both domestic and global markets.The test rig was inaugurated on March 5 in the presence of Andreas Evertz, Group CEO, Flender; Lars Wiegemann, Vice President Wind Gears, Flender; and Vinod Shetty, CEO, Flender India, along with key industry customers and stakeholders.The insta..