
Govt to revamp ship ownership and registration rules with new bill
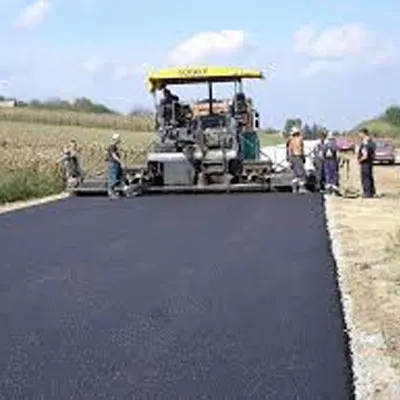

India Becomes First to Produce Bio-Bitumen for Roads
India has become the first country in the world to commercially produce bio-bitumen for use in road construction, according to Road, Transport and Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari. Bitumen, a black and viscous hydrocarbon derived from crude oil, is a key binding material in road building, and the bio-based alternative is expected to significantly improve the sector’s environmental footprint.Addressing the CSIR Technology Transfer Ceremony in New Delhi, Mr Gadkari congratulated Council of Scientific and Industrial Research on achieving the milestone, noting that the initiative would help curb ..
HILT Policy Seen Boosting Telangana Revenue Sharply
The Hyderabad Industrial Land Transformation (HILT) Policy is expected to generate around Rs 1.08 billion in revenue for the Telangana state exchequer, according to Deputy Chief Minister Bhatti Vikramarka Mallu. Speaking in the Telangana Legislative Assembly, he said the policy would be implemented within a six-month timeframe in a transparent manner, with uniform rules applicable to all stakeholders. Mr Vikramarka noted that without the HILT Policy, the state would have earned only about Rs 1.2 million per acre. Under the new framework, however, revenue is projected to rise sharply to Rs 70 ..
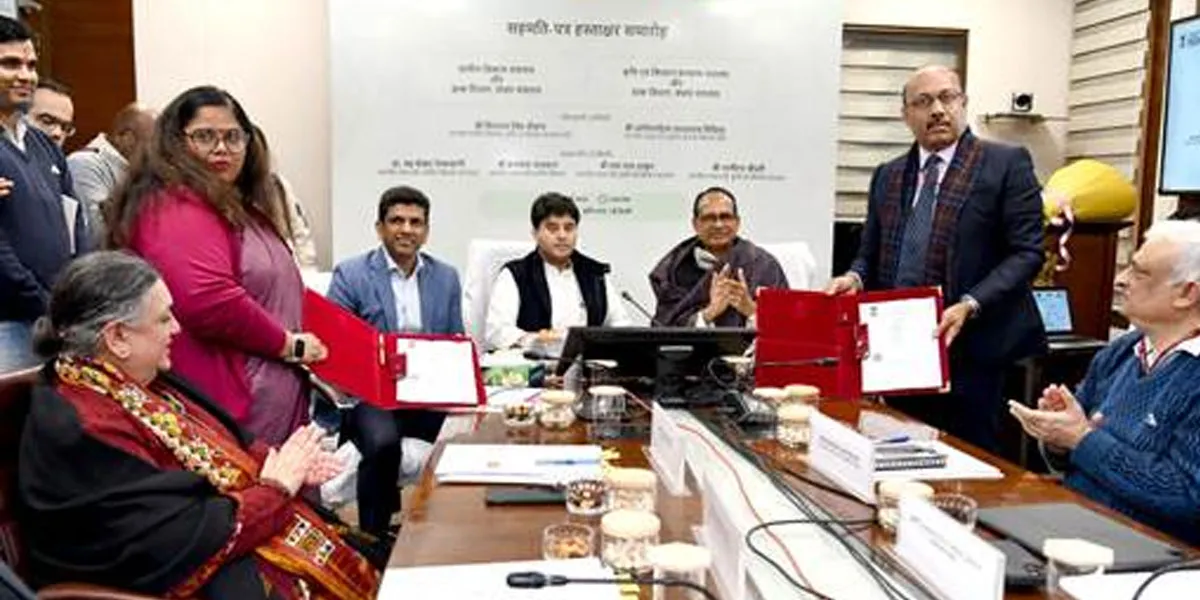

India Post, MoRD Tie Up to Boost Rural Inclusion
The Department of Posts and the Ministry of Rural Development have signed a Memorandum of Understanding to accelerate rural transformation and expand financial, digital and logistics services for Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and rural households across India. The agreement was signed in the presence of Union Minister of Communications and Development of North Eastern Region Jyotiraditya M. Scindia and Union Minister of Rural Development and Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare Shivraj Singh Chouhan. The collaboration aligns with the government’s “Dak Sewa, Jan Sewa” vision and seeks to repositi..
















