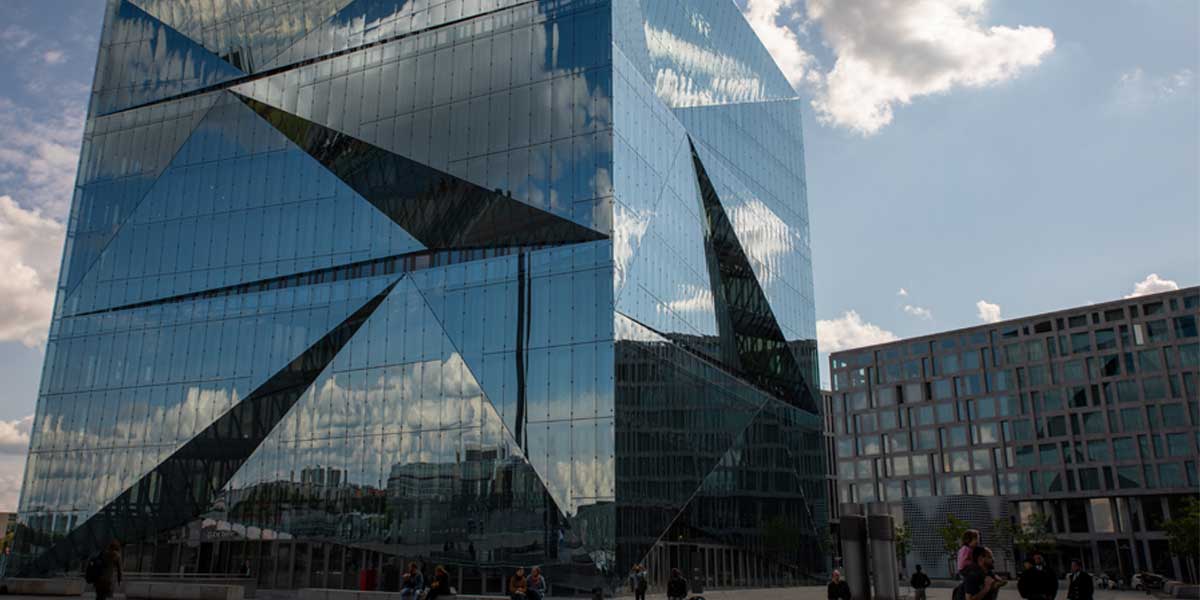
As the global conversation is turning sustainable, more and more designers and architects are choosing glass as a building material that has a far lesser carbon footprint in comparison to other materials.
According to Nitin Mehta, Co-Founder and Executive Director, ALCOI, “Envisioning a cleaner environment for a healthier world, the demand for green buildings is on the rise in the architecture community. Owing to the rapid depletion of natural resources, their scarcity and their negative impact on the environment, constructing an eco-friendly living space has become the need of the hour. Glass qualifies as an eco-friendly material because it is recyclable and can contribute significantly to mitigating climate change and saving precious natural resources.”
How glass improves sustainability?
One of the most versatile building materials, glass can be moulded in different shapes, sizes and strengths. It is durable and resists weather conditions.
A natural insulator, glass allows buildings to have green-house effect by increasing the heat value of natural light and keeping structures warm where needed. It also traps in the cooling of inner air-conditioners keeping homes or buildings cooler for a longer duration. This leads to lesser consumption of electricity and energy resources.
Flexibility of glass as a building material allows it to be carved in various shapes and designs. These processes use less pollutants for the environment as compared to any other material leading to a smaller carbon footprint on the environment.
Textures and treatments on glass can be easily done to create various definitions in any building. From glazed to translucent, from designed to plain, all kinds of treatments are possible on glass in lesser cost and impact on the environment, making it a sustainable choice.
“Glass being 100 percent recyclable, that too over and over again, is a sustainable material. In a sustainable design where we are trying to bring in natural light and ventilation into a building, glass gains utmost importance. It also helps reduce the weight of buildings in tall structures. It can also be used in many aesthetic ways, making it a very desirable element of sustainable design. Best part is, it can be easily cleaned and maintained, and hence serves as a hygienic surface” say Monica Chawla & Hardesh Chawla, Essentia Environments, Founders, Essential Environments.
Glass types used in construction of green buildings
Green buildings or sustainable buildings are designed to function in the best possible manner with the right balance between impact on the environment and the material used. Glass has been at the core of such buildings and multiple types of glass have been used in these to serve different purposes.
The Ecosense glass is designed specially keeping in mind the Indian subcontinental climate. It helps achieve a blend of aesthetics and economics, finesse and function. It prevents heat from entering a space, keeping it cooler than making it hot. It is an energy efficient solution as it allows natural light to pass through but not the heat that comes with it. This type of glass is mostly used on the exteriors of a building such as windows or facades and even skylights.
The Opal glass is a glass type that improves the aesthetics of a structure along with providing heat insulation. It is also used on the exteriors of facades, but more from the aesthetic point of view.
The Sunshield glass as the name suggests reduces glare by insulating the building and keeping them cool during harsh heat, making it energy efficient. One amongst the most sought after glass types, it also keeps the people in the building safe from harmful UV rays.
The Supersilver glass is achieved by a certain treatment of glass that results in a reflective surface. This is much lesser in cost as compared to spray-coated reflective glass products available in the market. It is customisable and easy to install inside the buildings and plays the role of reflecting light back making it both cost and energy efficient.
Designers and architects choose the glass to be used in any building based on its geographical location, orientation and the requirement of the structure to stay insulated, heat up or cool. Various treatments on glass allow it to become the most versatile, cost effective and eco-friendly building material that leaves the least amount of carbon footprint. Glass plays a key role in structure design as a sustainable building material.
“With technological advancements, insulation properties of windows and facades have improved drastically. Take the example of double and triple glazed units, which come with inert gas fillings and invisible low-emissivity coatings. These glazing products bring maximum natural daylight into buildings and increase or limit solar heat gains based on the desired thermal objectives and energy balance ``, says Mehta.
“In combination with shadow and ventilation systems, glass facades are highly efficient in keeping the interiors warm in winter and pleasant during the summers. The material meets the current generation’s desire for more transparency, allowing outward and inward views. Glass helps to build a seamless connection between the interiors and verdant outdoors. However, architects need to ensure that the buildings of tomorrow reflect the needs of our future, and it doesn't come at the cost of natural light in our living spaces” he adds.
Also read: