As
infrastructure ministries lay out ambitious plans to go the “InfraNirbharta”,
or infrastructure-dependence, route, a commendable method to get there is the
National Infrastructure Pipeline. Pratap
Padode explains how, but ends on a cautionary note.
_______
All through 2020, we urged the government
to relook at their priorities and prioritise infrastructure. We have written
open letters to the Finance Minister, sent letters to the Prime Minister, and
urged in several articles round the year. On 1 February 2021, the Union Budget
delivered sweet music to my ears. From Atmanirbhar
(Self-reliant) we morphed into InfraNirbhar
(infrastructure-dependent). The National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP),
which was seeming to turn into a pipe dream, catapulted back into the
reckoning.
Construction
World made inroads into the Ministry of Finance,
Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH), and Ministry of Housing
& Urban Affairs to gather first-hand intelligence into the seriousness and
the plan of execution.
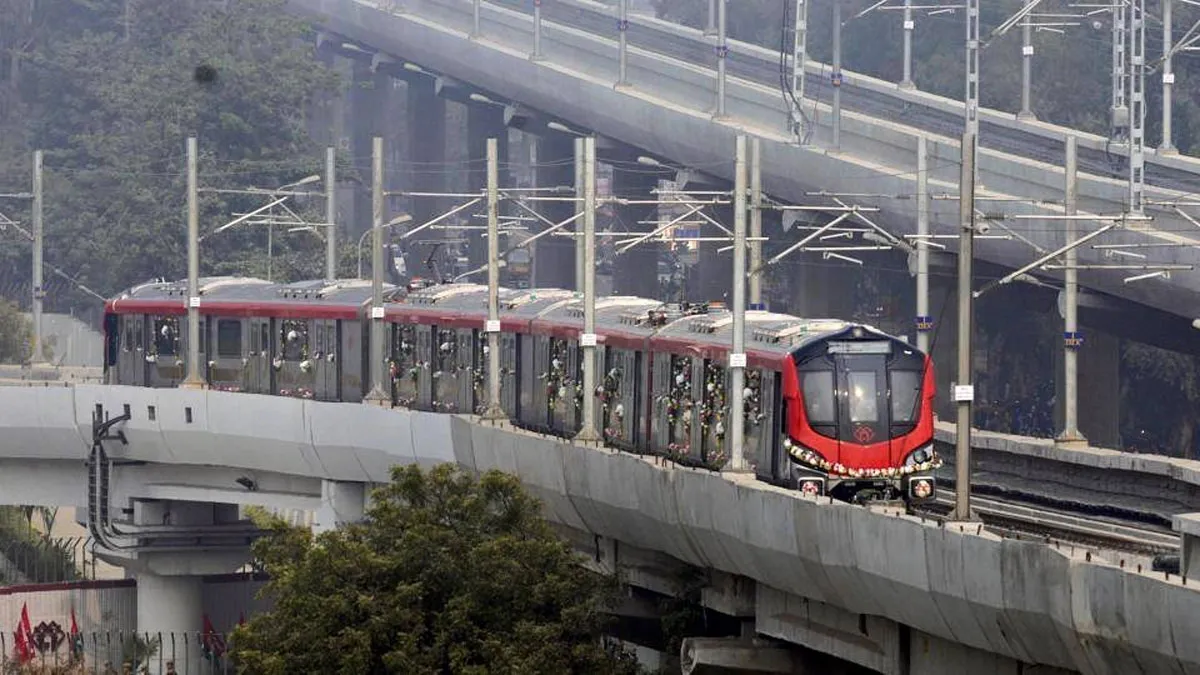
While Union Minister Nitin Gadkari is already
setting his sights on achieving the 40 km per day target, Minister of State for
Housing & Urban Affairs, Hardeep Singh Puri is laying the ground for
1,700 km of metro rail in 25 cities by 2025. The road to great infrastructure
is fraught with challenges. But Dr TV Somanathan, Secretary (Expenditure)
allayed the scepticism by acknowledging that although the plan depended on the
success of the asset monetisation programme and disinvestment, they had
prioritised and provided for additional funding towards meeting the enhanced
infrastructure expenditure required as per the NIP.
The setting up of a Development Fund for
infrastructure funding would provide long term finance and would currently leverage
on the low rates of interest trending due to a sea of liquidity in the global
markets. Somanathan admitted that the National Infrastructure Investment Fund
could not accomplish in entirety what they had hoped and hence the need to set
up this alternate institution. Deepening the bond market, which has been a
perennial demand, has also been put on priority.
The asset monetisation programme for MoRTH
is already underway, with Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs) set to
raise funds on existing toll yielding road assets. MoRTH Minister Nitin Gadkari,
not content with only scaling up his execution targets urged the
industry━including RS Mopalwar, the Managing Director of Maharashtra State
Road Development Corporation (MSRDC), which is currently executing the 701 km
Samruddhi Mahamarg between Mumbai and Nagpur━to create greenery, to consider
interventions like steel fibre as building material, crash barriers made of
bamboo, and such other material in improving sustainability.
The plans on metro rail are well-funded and
the need is to improve the number of passengers to improve viability. Metro Neo
Lite, a lighter version of the metro rail which also makes a smaller hole in
the pocket may be an answer to some of the smaller cities, which do not have
enough numbers to support a larger investment. The Andhra Pradesh Metro Rail
CEO Surjit Madan is exploring this option, and so are the Nashik Metro Rail
authorities.
India seems to be on its way to reform in
order to transform. There are tedious challenges in the ‘ease of doing
business’ area within infrastructure and we literally have miles to go. Legacy
issues will continue to keep bogging us down but if funding and sustainability
is on track these will evolve.
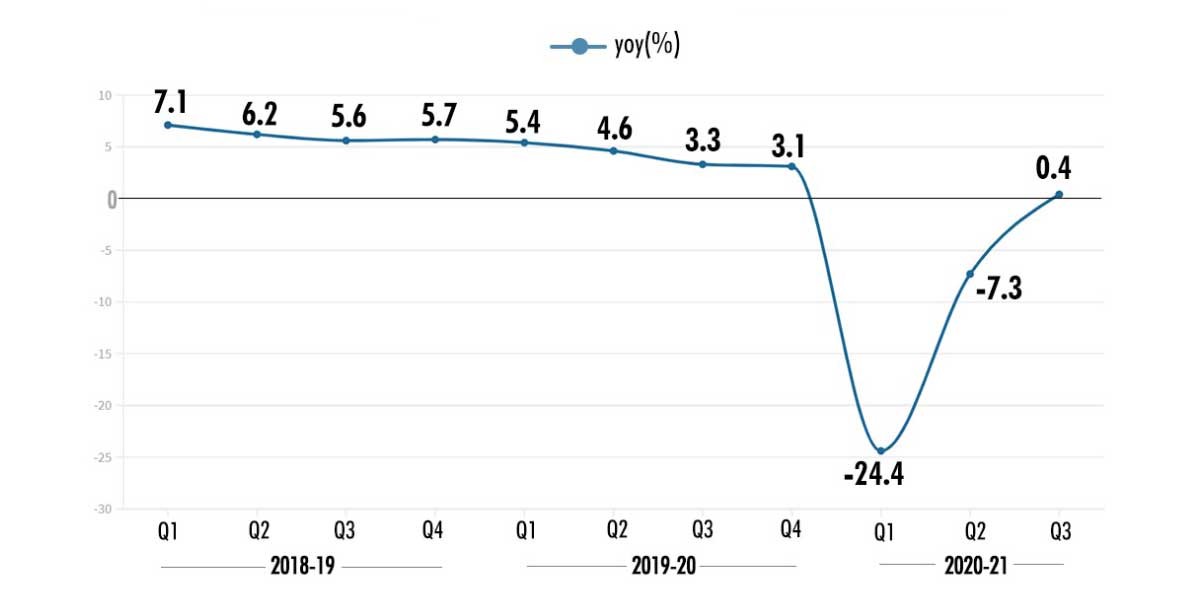
Meanwhile, a sharp rebound in construction
and manufacturing helped India's GDP record a marginal 0.4% growth in the
October-December quarter that also coincided with India’s festival season,
according to data released by the National Statistics Office (NSO) Friday. For
the full year, the NSO has forecast a steeper contraction of 8% than the 7.7%
forecast earlier. For the quarter ending December, construction recorded a
growth of 6.2% as against a contraction of 7.2% seen in the preceding quarter.
The financial, real estate and professional services was another sector that
saw a sharp revival—growing at 6.6% in the quarter as against a contraction of
9.5% in the previous quarter.
We are out of the recession but not out of
the woods yet.
Author: Pratap Padode is the Editor-in-Chief of Construction World and President of FIRST Construction Council.
Image source: MoSPI