
Debate emerges in govt over 500 GW RE target in new NDCs
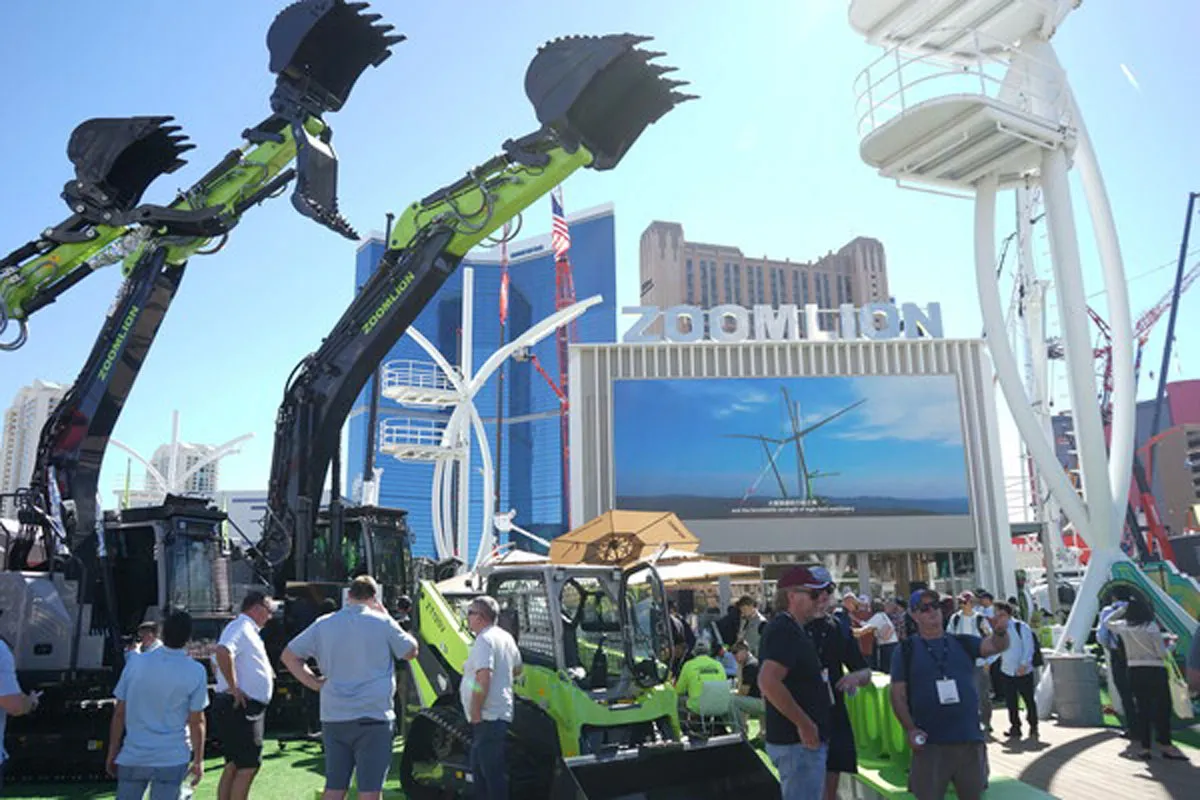

Company showcases North America-certified machinery and secures new deals
Zoomlion Heavy Industry Science & Technology Co., recently showcased a wide portfolio of North America-certified and customised construction equipment at CONEXPO-CON/AGG 2026 in Las Vegas. The display included engineering hoisting machinery, concrete equipment, earthmoving machinery, mining equipment and construction hoisting solutions tailored to regional operational requirements.All equipment presented at the exhibition complies with North American certification standards, with several models specifically developed to meet local regulatory requirements and site conditions. One of the hig..
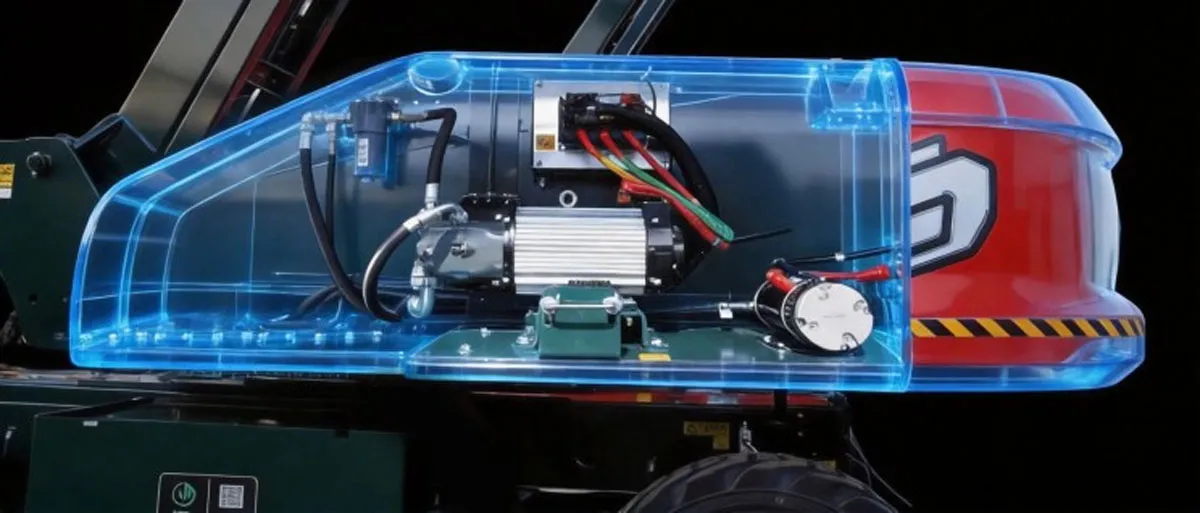
Sinoboom Launches Dual-ETM Smart Technology
Sinoboom recently introduced its Dual-ETM Smart Technology at CONEXPO-CON/AGG 2026, designed to enhance battery endurance and operational efficiency in electric boom lifts.The new technology integrates advanced components that enable real-time optimisation of power usage during equipment operation. By calculating the precise power requirement instantly, the system delivers only the energy needed for each movement, reducing the inefficiencies associated with conventional maximum-demand power systems.The solution incorporates multiple sensors—including pressure, weight, length and level sensor..

Ramky Infra Wins Rs 14.01 Bn DMIC Project
Ramky Infrastructure has secured an engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) contract worth Rs 14.01 billion from Maharashtra Industrial Township Limited (MITL) for infrastructure development in Phase 1 of the Dighi Port Industrial Area (DPIA) under the Delhi–Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC).The project, located in Raigad district of Maharashtra, involves comprehensive infrastructure works including design, engineering, construction, testing and commissioning, along with operations and maintenance. The contract includes a four-year operations and maintenance period after commissionin..

















